Databricks Apps present a sturdy platform for constructing and internet hosting interactive purposes. React is nice for constructing trendy, dynamic net purposes that have to replace easily and look polished. By combining this platform with a React-based frontend and Mosaic AI Agent Framework, builders can create environment friendly and clever chat purposes.This weblog focuses on the technical implementation of a Databricks-hosted chatbot and demonstrates its potential with an industry-specific Manufacturing Operations Administration Chatbot use case.
Databricks Apps and Mosaic AI Integration
The structure overview:
Core Strengths of Databricks Apps
Databricks Apps natively combine with:
- Databricks SQL: For querying giant datasets effectively.
- Unity Catalog: For centralized knowledge governance and entry management.
- Mannequin Serving: For deploying machine studying fashions at scale.
- Serving Endpoints: For environment friendly queries to the ML fashions and LLM brokers.
- Jobs: For ETL pipelines and workflow processes.
Databricks Apps get rid of the necessity for exterior internet hosting infrastructure. Functions inherit the platform’s built-in safety, compliance, and useful resource administration options, streamlining deployment and upkeep.
Databricks Apps assist a variety of frameworks akin to Sprint, Streamlit, Gradio, Flask, and FastAPI. This flexibility permits for each data-rich and visually participating purposes.
What’s Mosaic AI Agent Framework?
The Mosaic AI Agent Framework is a set of instruments on Databricks that helps builders create, deploy, and handle AI brokers, akin to these utilized in Retrieval-Augmented Technology (RAG). It integrates with frameworks like LangChain and LlamaIndex and makes use of Databricks options like Unity Catalog for knowledge governance and tool-calling.
Builders can log and take a look at brokers with MLflow, debug their conduct, and improve efficiency. Options like request logging, response token streaming, and overview apps make constructing and deploying AI brokers simpler for real-world use circumstances.
Use Case: Manufacturing Operations Administration Chatbot
Manufacturing Operations Administration (MOM) is essential for optimizing manufacturing processes, enhancing effectivity, and sustaining competitiveness in at present’s quickly evolving industrial panorama.
The demand for operation administration utilizing AI brokers with pure language interfaces is quickly rising, pushed by the necessity for elevated effectivity, improved decision-making, and enhanced consumer experiences.
In keeping with the newest publication from Meticulous Analysis® (supply), the AI in manufacturing market is projected to achieve $84.5 billion by 2031, at a CAGR of 32.6% throughout the forecast interval 2024–2031 [1]. This important development underscores the rising recognition of the significance of AI-driven operation administration in numerous industries.
A producing firm implementing the Mosaic AI chatbot leveraging tool-calling can help manufacturing managers in:
Bottleneck Evaluation
- Device perform: Queries Databricks SQL utilizing the
identify_bottleneck_stationperform to find out the station inflicting probably the most delays. - Instance question: “What’s the present bottleneck within the meeting line?”
- Response: “Station 5 is the present bottleneck, with a median delay of quarter-hour per cycle.”
Stock Monitoring
- Device perform: Calls
check_inventory_levelsto retrieve real-time inventory knowledge for a specified station. - Instance question: “Do we now have sufficient supplies for Station 3?”
- Response: “Station 3 has sufficient supplies for the subsequent 5 manufacturing cycles.”
These queries may be simply carried out as features saved in Unity Catalog, utilizing both SQL or Python. Then an AI agent can carry out duties akin to knowledge retrieval, code execution, and context-based decision-making by leveraging the perform calls. Whereas we gained’t dive into the specifics of establishing the agent for tool-calling right here, you’ll be able to confer with the Databricks Generative AI Cookbook right here for detailed steering.
As soon as the Mosaic AI agent is ready up and configured to deal with numerous instruments, it may be deployed as a model-serving endpoint on Databricks. This endpoint acts because the backend interface, permitting frontend purposes like chatbots to ship queries and obtain real-time insights.
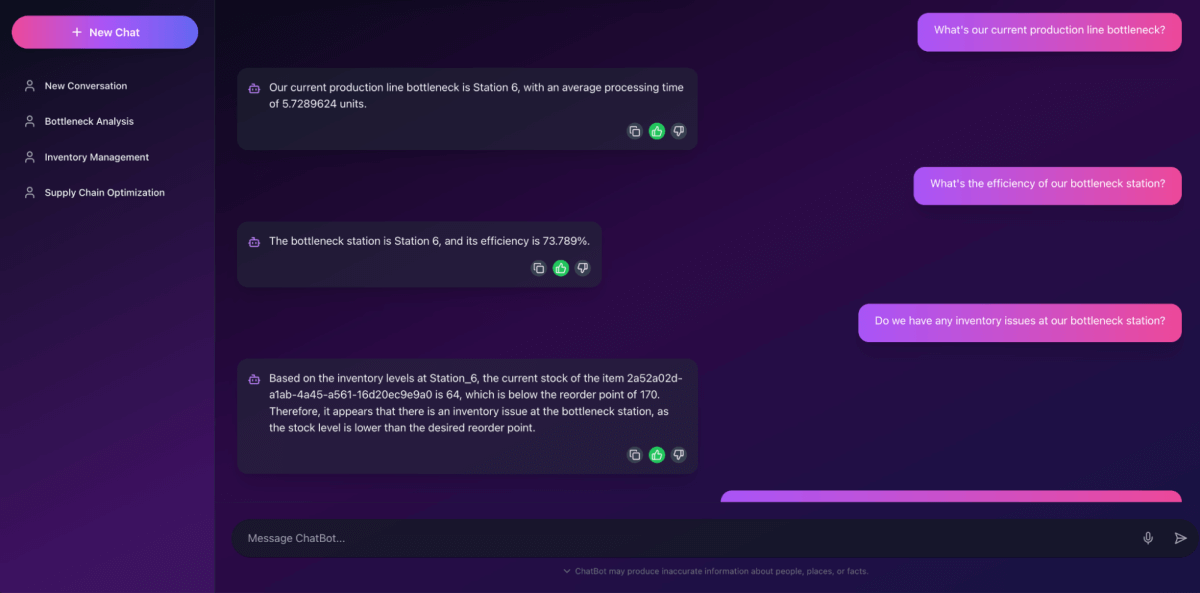
Right here is the chatbot interface operating regionally; later, we’ll display it after deployment to Databricks Apps.
Databricks Apps Implementation
1. Frontend with React
The React frontend offers an interactive and user-friendly interface for querying the chatbot and visualizing responses. Core options embrace real-time message rendering, question submission, and bot response dealing with, interactive UI with suggestions, and Markdown assist.
Frontend Code Sending Messages to the Backend
API Shopper: Axios is used to make HTTP requests. The baseURL is dynamically set based mostly on the atmosphere (growth or manufacturing).
HandleSendMessage: It captures consumer enter, sends the message to the /api/chat API endpoint, and updates the chat historical past with each consumer and bot messages.
2. Backend with FastAPI
The FastAPI backend serves because the bridge between the React frontend and Mosaic AI brokers. It routes consumer queries to the agent’s model-serving endpoint to get a response.
Backend Code Dealing with Consumer Queries
This API endpoint receives consumer messages, interacts with the Mosaic AI agent model-serving endpoint, and returns task-specific responses.
In FastAPI, the order of mounting sub-applications is essential as a result of it determines how incoming requests are routed.
app.mount("/api", api_app):
- This mounts a sub-application (
api_app) on the/apiroute. - Any request beginning with
/api(e.g.,/api/chat) is routed to this sub-application. - This ensures that each one API-related requests are processed by the
api_appoccasion.
app.mount("/", ui_app):
- This mounts the static recordsdata from the
shopper/constructlisting on the root (/) route. - That is sometimes used to serve the compiled frontend utility, which embrace
index.html, JavaScript, CSS, and different static property. Many of the main UI frameworks (e.g. React, Vue and Svelte) assist compilation into such a set of property by way of totally different bundlers (e.g. Vite, Webpack or esbuild). - Any request that doesn’t begin with
/apican be routed to theui_app.
- API Setup and Endpoint Definition: The code defines a FastAPI utility with a POST endpoint (
/chat) beneath theapi_appoccasion that factors to the Mosaic AI agent’s model-serving endpoint on Databricks. - Dependency Injection and Request Dealing with: The endpoint makes use of FastAPI’s dependency injection mechanism (
Relies upon) to inject aWorkspaceClient, which is chargeable for interacting with Databricks APIs. Thechat_with_llmperform takes aChatRequestcontaining the consumer’s message, codecs it as aChatMessagewith the positionUSER, and sends it to the serving endpoint utilizing theshopper.serving_endpoints.questionmethodology. - Response Parsing and Return: The response from the agent is structured and returned as a
ChatResponseto the shopper.
Deployment on Databricks Apps
1. Getting ready the Backend
- Place the FastAPI code in an
app.pyfile. - Outline dependencies in
necessities.txt:
- Create an
app.yamlfile:
The command part outlines the gunicorn server configuration with the next specs:
- server.app:app: Runs your FastAPI utility.
- -w 2: Makes use of two employee processes to deal with incoming requests.
- uvicorn.staff.UvicornWorker: Makes use of Uvicorn staff, that are appropriate with FastAPI’s ASGI framework.
The env part specifies key-value pairs that outline atmosphere variables to cross to the app [2]:
- title: the title of the atmosphere variable.
- valueFrom: For an externally outlined worth, the title of the supply containing the worth. For instance, the title of a secret or a database desk containing the worth.
I’m mapping the atmosphere variables SERVING_ENDPOINT_NAME to the Databricks useful resource model-serving endpoint agent_MODEL_NAME_FQN, the place MODEL_NAME_FQN represents the three-level namespace of Unity Catalog for catalog.db.model_name.
2. Getting ready the Frontend
- Construct the React app with
npm run constructand place the static recordsdata in/shopper/construct.
Right here is the file construction:
3. Deployment Steps
- Create the Databricks App:
- Configure Databricks Sources:
I’m establishing the Databricks sources to align with the options outlined within the env part of the app.yaml file. This consists of configuring sources such because the model-serving endpoint (agent_MODEL_NAME_FQN).
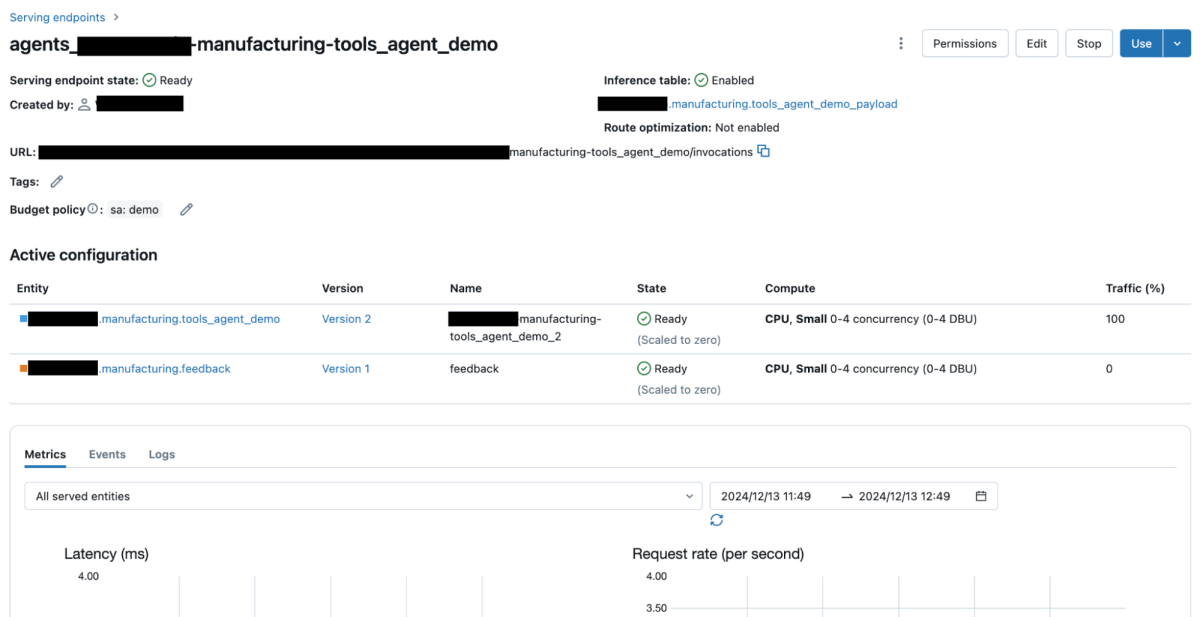
The under picture reveals that the chatbot app has been efficiently created: - Sync Information:
- Deploy the App:
After executing this command, the deployment course of will take a couple of minutes. As soon as efficiently deployed, the Databricks App’s URL can be displayed, indicating that it’s up and operating.
And you can begin chatting with it. For instance, our manufacturing effectivity is low. Discover the bottleneck, verify its effectivity, and generate an in depth report. Ship an e-mail to [email protected] with the report. Additionally analyze the sentiment of the report.
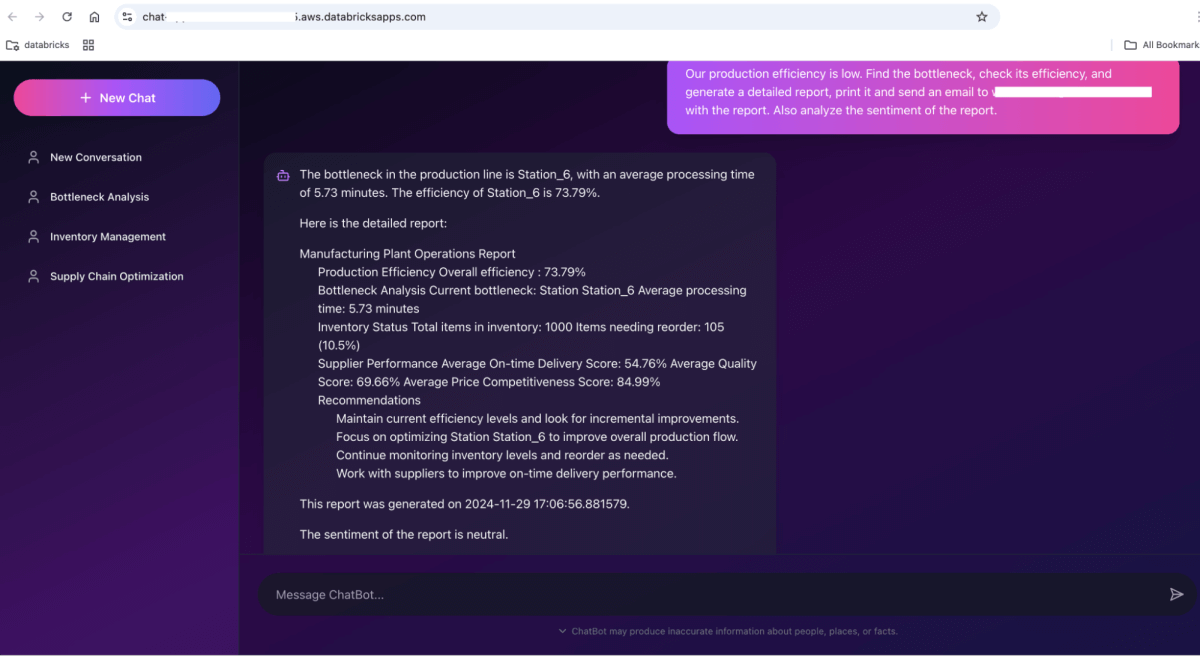
Conclusion
Integrating Databricks Apps with React and the Mosaic AI Agent Framework provides a strong answer for creating dynamic, interactive chat purposes. By leveraging Databricks’ built-in knowledge processing capabilities, safe model-serving, and streamlined deployment infrastructure, builders can construct strong programs that deal with advanced queries.
The usage of FastAPI as a bridge between the React frontend and Mosaic AI brokers ensures seamless communication. Whereas Databricks Apps assist numerous Python backend frameworks akin to Flask and Django, FastAPI was chosen for its concise and developer-friendly API.
This setup showcases how superior AI capabilities may be built-in into sensible {industry} options, akin to manufacturing chatbots, to drive effectivity and decision-making. As Databricks continues to evolve its platform, these integrations can develop to cater to broader use circumstances, making it a vital instrument for companies aiming to innovate with AI-driven options.
To reference the supply code, please discover the GitHub repository linked right here.
References:
[1] AI in Manufacturing Market to Attain $84.5 Billion by 2031. Supply:
https://www.meticulousresearch.com/pressrelease/294/ai-in-manufacturing-market
[2] Databricks Apps configuration. Supply:
https://docs.databricks.com/en/dev-tools/databricks-apps/configuration.html#databricks-apps-configuration
Integrating Databricks Apps with React and the Mosaic AI Agent Framework provides a strong answer for creating dynamic, interactive chat purposes. By leveraging Databricks’ built-in knowledge processing capabilities, safe model-serving, and streamlined deployment infrastructure, builders can construct strong programs that deal with advanced queries.

